DO YOU HAVE IT?
April 24, 2023
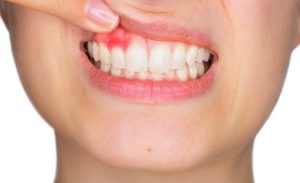 You’ve heard it before – three in four adults over 35 have some form of gum disease. A preponderance of clinical research reveals that gum disease poses a far greater threat to health than just losing a tooth. Periodontal disease may actually increase your risk for a variety of health concerns including heart attacks, low birth weight babies, diabetes, stroke, and other bad things.
You’ve heard it before – three in four adults over 35 have some form of gum disease. A preponderance of clinical research reveals that gum disease poses a far greater threat to health than just losing a tooth. Periodontal disease may actually increase your risk for a variety of health concerns including heart attacks, low birth weight babies, diabetes, stroke, and other bad things.
Dr. Isadore Rosenfield, noted cardiologist and media health consultant once said – “People with chronically infected gums have twice as much heart disease as the rest of us. We have an imperative to treat gum disease – to save not only teeth but also patients.”
Dr. Steven Offenbacher, former director of the Center for Oral and Systemic Disease at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill – “In many ways, periodontal disease is like high blood pressure – it’s painless and only becomes evident when it’s quite severe.”
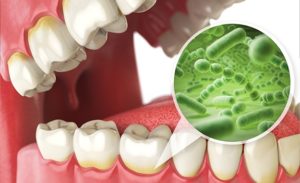
All gum disease begins with the accumulation of plaque, a sticky deposit of bacteria, mucus and food particles that build up along the gum line and between the teeth. Plaque can cause gingivitis – inflammation of the gums. Plaque must be removed daily to prevent buildup. Excellent home care, coupled with a minimum of twice-yearly professional cleanings, will combat gingivitis in most people.
There is a strong genetic component to periodontal disease. One of the questions I always ask my patients is whether or not they know their familial history with regards to gum disease. If a patient says that both of their parents had dentures, for example, there is a stronger likelihood that the patient carries the gene for gum disease. There are two main reasons that people lose teeth – gum disease and decay. Decay is 100% preventable. Gum disease, like diabetes, is controllable but not curable; it requires intervention.
If gingivitis is not treated, or is not treated soon enough, the result can become periodontitis. This occurs when plaque invades beneath the gum, turning into a hard substance called tartar or calculus. Calculus can only be removed during a professional cleaning. At this stage, skilled care is essential to stave off tooth loss. In more advanced cases, a procedure called scaling and root planning (aka deep cleaning), is performed to remove hidden plaque and tartar from below the gum line.
Do you have gum disease? Warning signs may not be evident to you but may include red, swollen, tender, bleeding or receding gums, loose teeth, persistent bad breath, changes in tooth position, and the development of pockets between gums and teeth. Having said that, if you have any of those symptoms, you’ve waited too long.
For most people, good health requires investment. Today, periodontal disease can be successfully treated BEFORE teeth get loose from bone loss. Your hygienist can measure the pockets and bleeding points around your teeth and institute non-surgical treatment before you suffer the irreversible bone destruction of periodontal disease.
So, remember two things: First, lack of pain is NOT a good indicator that you don’t have problems – Second, the hygienists of the 21st century don’t just clean teeth – they save lives!
The mouth is the gateway to the rest of the body; take good care of it.
Dr. St. Clair maintains a private dental practice in Rowley dedicated to health-centered family dentistry. He has a special interest in treating snoring, sleep apnea and TMJ problems. If there are certain topics you would like to see written about or questions you have please email them to him at jpstclair@stclairdmd.com
ORAL HEALTH IS ESSENTIAL
April 18, 2023
 What is your definition of oral health? Is there even a standard definition of oral health? One thing is clear; the definition of oral health is not solely the absence of pain. Pain is also not necessarily an indication of poor oral health.
What is your definition of oral health? Is there even a standard definition of oral health? One thing is clear; the definition of oral health is not solely the absence of pain. Pain is also not necessarily an indication of poor oral health.
It wasn’t until the year 2000 that oral health was brought to the forefront of the surgeon general’s report as a critical component to overall health. This was an important event, but unfortunately never amounted to much in terms of being incorporated into most healthcare policies. This has led to continued poor to non-existent cross-over coverage between medical and dental insurance.
In 2005 at the World Congress of Preventive Dentistry, participants from 43 countries made it clear that oral health is an integral part of general health and overall well-being. They even concluded that oral health is a basic human right.
More recently, the United Nations recognized oral disease as an integral part of other non-communicable diseases such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, stroke, chronic respiratory diseases and cancer. This association with these other diseases was based on common social determinants such as socioeconomic status, diet, tobacco and alcohol use, and not on the basis of transmission. However, there is still no solid definition of what oral health really is.
According to a column in the Journal of the American Dental Association, the American Dental Association is working on a proposed definition of oral health. The authors of the column state, “A proposed definition is necessary to achieve a common understanding of the scope of oral health, to help understand the array of complex oral and systemic health issues facing dental and medical professions now and, in the future, and to provide a rationale to position oral health professionals as partners within primary health care.”
The authors go on to say that the definition of oral health needs to align with the current definition of dentistry. That definition currently states, “dentists are responsible not only for the evaluation, diagnosis, prevention and treatment of diseases and conditions of the oral cavity, the maxillofacial area and adjacent areas but also for assessing their impact on the human body.”
As new tests and knowledge in the area of oral health increases, the days of simply recording missing and decayed teeth and poking patients with instruments to chart periodontal (gum) issues may not be enough to best serve patients. What we can learn from things such as genetic testing and salivary diagnostics will change the way we interact with our medical colleagues and greatly benefit our patients.
In conclusion, the authors state, “As the definition of oral health evolves and likely will continue to evolve well into the future, no matter how oral health is defined, the message remains: Oral health is essential to an individual’s general health and quality of life.”
So, while the powers that be work on the definition of oral health, it is our individual responsibility to take care of ourselves. If we know that oral health is connected to the rest of the body and if we care enough to take care of our body, then regular professional maintenance and constantly improving our home care should be at the forefront of our self-care.
Dr. St. Clair maintains a private dental practice in Rowley dedicated to health-centered family dentistry. He has a special interest in treating snoring, sleep apnea and TMJ problems. If there are certain topics you would like to see written about or questions you have please email them to him at jpstclair@stclairdmd.com
ALWAYS ROOM FOR IMPROVEMENT
April 10, 2023
 I have had a few patients ask recently about the order of oral hygiene activities. Does it matter if you brush or floss first, and should this be done before or after breakfast? Based on available research, it seems opinion matters as much as scientific facts.
I have had a few patients ask recently about the order of oral hygiene activities. Does it matter if you brush or floss first, and should this be done before or after breakfast? Based on available research, it seems opinion matters as much as scientific facts.
A spokesman for the American Dental Association and a professor of restorative dentistry at the University of California, Los Angeles, recommends flossing first. His rationale? Get the unpleasant task out of the way to avoid the temptation to not do it. “Let’s face human nature, if you’re going to skip one, which one will you skip?”
By contrast, a professor of oral health sciences at the University of Washington in Seattle, advises her patients to brush with a fluoride toothpaste, then floss. She says that way your mouth will be awash with fluoride as you are maneuvering the floss.
So, what’s my opinion? I was taught and have always maintained that flossing before brushing is better. The rationale behind this is that plaque and other debris is dislodged during the act of flossing allowing toothpaste and the mechanical action of brushing to better penetrate the different surfaces of the tooth. Does it really matter? I don’t think so.
Have you heard your dental hygienist or dentist tell you to floss to prevent cavities between your teeth? Based on research, the main reason for flossing is not for prevention of cavities. Rather, flossing’s main benefit is stimulation of tissue to reduce gum inflammation known as gingivitis. Gingivitis can lead to more advanced gum disease and things like bad breath. That is why I believe that regular use of a water pik and an electric toothbrush is most ideal.
A review of 12 randomized controlled trials found that people who brushed and flossed regularly had less gum bleeding than the brush-only camp. No surprises there. There have been no studies, that I am aware of, reporting a reduction in cavities from flossing. Of course, these are difficult studies to conduct. There are many factors that contribute to decay occurring between the teeth.
There are also different schools of thought whether to brush and floss before or after breakfast. I don’t know about you, but I cannot eat or drink anything (especially orange juice) after I brush my teeth. So, although you might expect the solution to be brushing after breakfast, there is some risk with that.
If you eat or drink something sugary or acidic—like the fruits, juices, and other breakfast foods many of us eat in the morning— the mouth is in an acidic environment for at least 30 minutes after consumption. These acids weaken tooth enamel, and brushing too soon can cause damage to the enamel. If you know you’re going to eat or drink something very acidic ahead of time, you may want to brush your teeth first.
Alternatively, you can wait 30 minutes after you eat for your saliva to neutralize the pH of your mouth. Or, re-balance your oral pH right away with an alkaline mouth rinse and then brush. In the end, it depends a little on what you eat. Take stock of what you’re eating for breakfast and judge when you should brush based on its sugar or acid content.
Everyone, well…..almost everyone, can stand some improvement with their oral hygiene. Many dental problems are completely avoidable with excellent home care, which is in your control. Ask your dentist or hygienist how to improve your home care. Strive for constant improvement.
Dr. St. Clair maintains a private dental practice in Rowley dedicated to health-centered family dentistry. He has a special interest in treating snoring, sleep apnea and TMJ problems. If there are certain topics you would like to see written about or questions you have please email them to him at jpstclair@stclairdmd.com
THE SILENT EPIDEMIC
April 3, 2023
 Last week I talked about a sometimes not so silent epidemic – sleep apnea. This week’s epidemic is much quieter but shares the general idea of decreasing the quality of life.
Last week I talked about a sometimes not so silent epidemic – sleep apnea. This week’s epidemic is much quieter but shares the general idea of decreasing the quality of life.
With more than 24 million diabetics and 57 million pre-diabetics in the United States, there are a lot of people affected by diabetes. That’s nearly a quarter of the nation’s population. The most up to date research shows the connection between dental health and diabetes has never been more critical.
As an indication of our general health, the rapidly rising rate of diabetes should be ringing alarm bells everywhere. The litany of health implications from diabetes is a long and grisly list. It is the sixth leading cause of death in the U.S. That is probably vastly understated because as many as 65% of deaths from diabetes are attributed to heart attack and stroke. People with diabetes have about twice the overall risk of death as those who don’t have the disease.
Complications from diabetes cut years off productive lives and interfere with the quality of those lives through a host of debilitating health effects. Heart disease and stroke rates are as much as four times higher among diabetics. Nearly three-quarters of diabetics have high blood pressure. Each year, diabetes causes blindness in as many as 24,000 Americans. It is the leading cause of kidney failure, nervous system disease, amputations – the list goes on.
The facts about the connections between oral health and diabetes are even more alarming than those about diabetes alone. Here are just a few:
Diabetics are twice as likely to develop gum disease. This is especially true if your diabetes is not under control. The gum disease then worsens your diabetes through an automatic response that your body uses to fight the infection.
People with gum disease are 270% more likely to suffer a heart attack than those with healthy gums.
People who have diabetes and severe gum disease have a premature death rate nearly eight times higher than those who do not have periodontal disease.
Those who have gum disease and diabetes together are more than three times more likely to die of combined heart and kidney failure.
In people who have type 2 diabetes, gum disease is a predictor of end-stage kidney disease.
In people who have pre-diabetes – blood glucose levels that are higher than normal but not in the diabetic range – gum disease makes it more likely that they will become diabetic.
Once established in a person who has diabetes, the chronic infection that causes gum disease makes it more difficult to control diabetes, and increases damage and complications in blood vessel disease.
These are simply the facts and, yes, they are sobering. If you have diabetes or are pre-diabetic, make sure you are doing all you can to control these diseases. These two diseases can twist each other into a tight downward spiral of amplifying negative health effects. Unless they are halted by your physician and your dentist working in tandem as a health care team, together with your commitment to hold up your end of the bargain, these effects can continue to compound.
Dr. St. Clair maintains a private dental practice in Rowley dedicated to health-centered family dentistry. He has a special interest in treating snoring, sleep apnea and TMJ problems. If there are certain topics you would like to see written about or questions you have please email them to him at jpstclair@stclairdmd.com